Ash5 What Best Describes the Electronic Geometry of the Molecule
If all of the electron pairs surrounding the central atom are shared with neighboring atoms then the coordination geometry is the same as the molecular. For any chemical system the goal of breaking or making bonds is to decrease or increase the overall potential energy of the system.

So32 Molecular Geometry Shape And Bond Angles Molecular Geometry Chemistry Help Molecular
Molecular Structures 285 O H H c OC O.

. View Available Hint s Submit Part D Which choice best. Since electron pairs repel molecules adjust to their shapes so that the electron pairs are as far apart. In order to find out the hybridization of such a molecule we will be using the formula.
Electron Geometry Hybridization Molecular Geometry VSEPR class Approximate Bond Angles 2 2 0 Linear sp Linear AX 2 180 3 0 Trigonal Planar AX 3 2 1 Bent AX 2 E 4 0 Tetrahedral AX 4 3 1 Trigonal Pyramidal AX 3 E 2 2 Bent AX 2 E 2 120 4 1095 3 Trigonal Planar. -a pi bond concentrates electron density along the axis between two nuclei. Four bonds on one central atom with bond angles of 1095.
Third the electron-pair geometry is determined by assigning the steric number to the central atom. First the steric number of the central atom is. A chemical formula that describes the makeup of a single molecule.
The number and type of electron domains is obtained from the Lewis structure. The placement of the two sets of unpaired electrons in water forces the bonds to assume a tetrahedral arrangement and the resulting HOH molecule is bent. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with six pairs of electrons is octahedral.
Other Apps - April 13 2022 Benefits Risks and Best Practices. And six regions form an octahedral geometry. B The molecule contains only one bond.
The molecular geometry is the geometrical arrangement of the atoms around the central atom. Using VSEPR theory predict the molecule shape of a molecule that contains 2 electron groups. Which of the following molecules has a tetrahedral shape.
AJR Ch10 Molecular Geometrydocx Slide 4 Octahedral The number and type of electron domains control the geometry. 4Describe the difference between writing Lewis Structures for ionic and covalent compounds. Triangular and in one plane with bond angles of 120.
Ash5 What Best Describes the Electronic Geometry of the Molecule. Part A What is the electron geometry of BrF5. Follow the systematic plan for Lewis structures given in the answers to Question 816 then determine the number of bonded atoms and lone pairs on the central atom det ermine the designated type.
View Available Hint s square pyramidal Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect. A The central atom P has five valence electrons and each fluorine has seven valence electrons so the Lewis structure of PF 5 is Figure PageIndex6. Two regions of electron density around a central atom in a molecule form a linear geometry.
Enter the molecular geometry of. The shape geometry that is always an exception to the octet rule. As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry changes to square pyramidalfive bonding and one nonbonding to square planar four bonding and two nonbonding.
Describe the Advantages of Using Annotated Statutes. Ash5 What Best Describes the Electronic Geometry of the Molecule. Three in a plane with bond angles of 120 and two on opposite ends of the molecule.
5Write out the steps involved in writing a Lewis Structure for molecular covalent compounds. We often refer to this atom as the central atom even if this atom is not really located at the geometrical center of the molecule. Draw a complete line-bond or electron-dot formula for acetic acid and then decide which statement is incorrect.
The HBeH molecule in which Be has only two electrons to bond with the two electrons from. An example of this geometry is SF 6. Three regions form a trigonal planar geometry.
The electron geometry and the molecular geometry are the same when every electron group bonds two atoms together. Well as the federal laws appear in more than one commercially published version. The electron geometry is the geometrical arrangement of the electron groups around the central atom.
Which is the best description of a molecule. What is the molecular geometry of the following molecule. D One carbon is described by sp 3 hybridization.
After performing many tests designed to reveal the shapes of various molecules chemist develop two different theories to explain certain aspects of their. Based on valence bond theory which statement best describes the electron geometry and hybridization of the central atom s in acetylene. Coordination number refers to the number of electron pairs that surround a given atom.
5 attempts remaining Part B What is the molecular geometry of BrF5. Anonymous C All electron groups are bonding pairs so PF 5 is designated as AX 5. Notice that this gives a total of five electron pairs.
Three of the chlorine atoms are in the plane of the central phosphorus atom equatorial positions while the other two atoms are above and below this plane axial positions. Explain why the HOH molecule is bent whereas the HBeH molecule is linear. Which of the following statements correctly describe a pi bond.
HF NH3 CH2F2 HCN CH20. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both trigonal planar. The polarity of each bond along with the geometry of the molecule determines the _____.
A One carbon is described by sp 2 hybridization. Write Lewis Structures for a list of formulas and identify their shape. Note that B can also be assumed to be bivalent easily.
What best describes the molecular geometry of the molecule. Ash5 Pe_ElianCalhoun828 April 19 2022. There are two general situations either the central atom which controls the geometry has non-bonding electrons lone pairs or it does not.
Five regions form a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. What best describes the electronic geometry of the molecule. Five atoms around the central atom.
-a pi bond holds two electrons one in. 12 x number of valence electrons in central atom number of the monovalent atoms attached to the central atom 12 x 53 4. Describe the molecular geometry.
Four regions form a tetrahedral geometry. Also describe the electron pair geometry. The shape of PCl 5 and similar molecules is a trigonal bipyramid.
Molecular bond angles Describe the orbitals that contain the valence electrons of a molecules atoms. -a pi bond is formed by the side-to-side overlap of two p orbitals. Enter the electron geometry of the molecule.
The electron geometry of the 2 carbons in acetylene is linear with a sp hybridization. Physical Chemistry Bonding Flashcards Quizlet To view the full text of the section click its citation. C The molecule contains four lone pairs of valence electrons.
This implies that the atom is sp3 hybridized. This consists simply of two triangular-base pyramids joined base-to-base.

Strong And Weak Acids Bases Chemistry Classroom Ap Chemistry Teaching Science
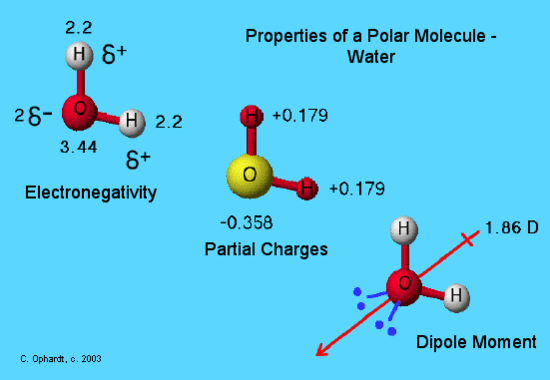
3 7 Geometry And Dipole Moment Chemistry Libretexts

No comments for "Ash5 What Best Describes the Electronic Geometry of the Molecule"
Post a Comment